Artificial intelligence, or AI, has quickly transitioned from a cutting-edge feature to a must-have capability. With open-source tools like TensorFlow and PyTorch, data science has become more accessible. At the same time, new cloud-based services, such as AWS AI Services, have made it even easier for developers to implement these capabilities.
Let's look at some popular AI use cases and how you can incorporate these technologies into your applications.
Artificial intelligence has quickly transitioned from a cutting-edge feature to a must-have capability. We look at the best way to get started! Share on XCommon Use Cases
Artificial intelligence has come a long way over the past decade. With the rise of deep learning, AI and machine learning technologies have become far better at everything from tagging people in a photo to predicting optimal inventory levels. These capabilities have quietly revolutionized many industries with a far superior user experience.
For example, IBM Watson teamed up with Behr to deliver custom paint color recommendations to customers through a one-on-one chat. These scalable personalized recommendations resulted in more than three times as much facetime with customers and more than twice the company's prior level of engagement with customers.
Some of the most common AI use cases include:
- Personalization: You can analyze a user's behavior and purchase history to predict products and services they're likely to buy. For example, Netflix leverages AI to predict shows you'll enjoy to maximize engagement.
- Document Processing: You can extract data from loan applications, medical forms, and other documents without manual effort. For instance, Amazon built out a massive database of book content by scanning pages one by one.
- Intelligent Search: You can make it easier to get information from siloed and unstructured data sources. For example, businesses might use AI to find data across disparate IoT platforms or across different factories.
- Fraud Detection: You can automatically flag fraudulent transactions based on historical data and other external factors. For example, many payment processes use AI to detect fraudulent transactions and automatically void them.
- Business Forecasting: You can streamline supply and demand decisions with historical time series data and product variables. For example, e-commerce shops might forecast optimal inventory based on past purchasing behaviors.
Of course, there are countless other ways that AI could be integrated into an application depending on the application and its customers. If you’re developing an application, the odds are that there are ways that AI could help improve them—it’s just a matter of finding the right areas to target and the right AI algorithms to deliver value.
Planning an Implementation
The best starting point for incorporating artificial intelligence into your application is identifying where it could provide the most value. For example, are you struggling to show relevant search results on your site search? Or, would it be more convenient for users to upload scanned documents rather than manually input the data into a form?
The next step is determining the best approach to implement AI. Many open-source and commercial tools make it easy for data scientists to build, train, and deploy machine learning models. While these tools can help develop proprietary models, the trade-off is that you'll need a team of experienced data scientists to build and maintain the models.
TensorFlow isn’t necessarily easy for developers to learn. Source: TensorFlow
Ready-built AI services are an even more accessible option for developers to add AI capabilities to their applications. Rather than building and training their own model, these services provide models trained on existing data sets and customer usage, providing a high level of functionality with far less data science overhead.
The final step is maintaining the technology over time. Often, the accuracy of AI predictions depends on their access to learning datasets. These datasets must be cleaned and prepared before being fed into models to maximize their value. In addition, you must always look out for biases that may creep up in the data, potentially invalidating the results.
Cloud-based AI Tools
There are a growing number of software-as-a-service businesses offering cloud-based AI tools. While Amazon AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure provide generic and specific AI solutions, many smaller individual providers also focus on niche markets, such as fraud identification, document processing, or business forecasting.
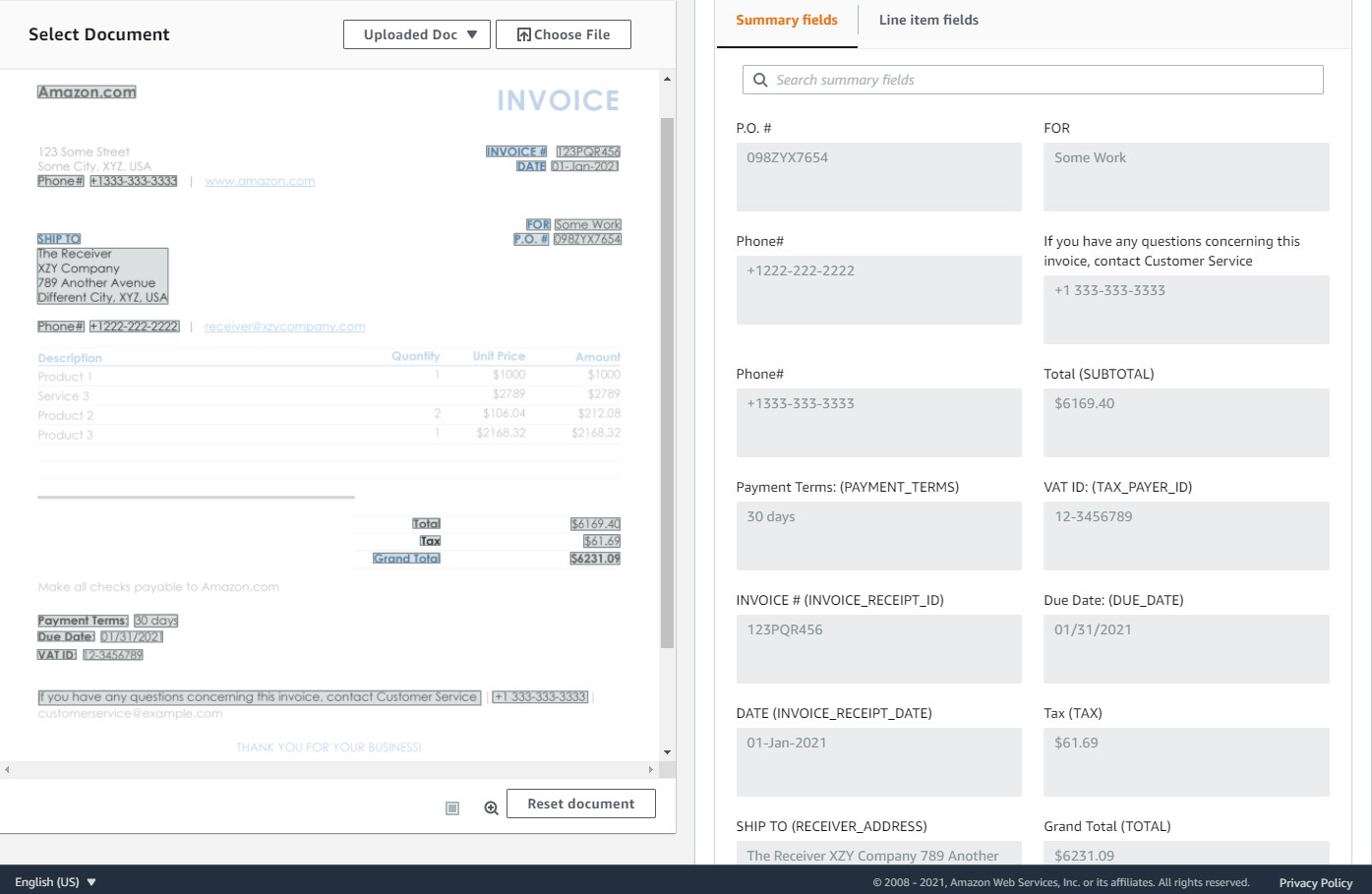
Amazon Textract automates document analysis. Source: AWS
There are several factors to keep in mind when choosing a solution:
- Price: The price of cloud-based AI tools varies based on the provider. For example, some companies have variable pricing based on usage or data volume, while others have a monthly fee to license an already-trained model.
- Support: Customer support may be valuable for teams that are new to AI or those that require help with implementation. While many companies provide pre-built integration libraries, some can be more complex to implement than others.
- Reliability: Many cloud-based AI tools provide APIs to communicate with applications, which means that reliability is critical to long-term success. If the API goes down, users could be left without AI predictions, causing a severely degraded user experience.
In some cases, you may choose to go with a provider that you’re already using for other services. For example, Amazon AWS’ AI Services may be a compelling option if you’re already using AWS for hosting or other purposes. You can keep all of the billing in one place and the services tend to work better together with ample documentation to help.
Business Model Impact
The addition of artificial intelligence-powered features could help justify premium subscription plans or addons to drive revenue and margins. In some cases, they could even lead to a change in a business model. You should carefully consider the implications of adding AI beforehand to identify these kinds of potential opportunities.
Some examples of these kinds of opportunities include:
- A language learning application might use AI to provide real-time translation, opening the door to entirely new ways to teach language learners.
- A tax planning application might automatically capture values from receipt photos to track business expenses in a premium plan.
- A delivery app might use machine learning to forecast supply and demand in order to optimize pricing levels and profits.
The Bottom Line
Artificial intelligence has quickly evolved over the past decade. While the technology is complex below the surface, there are numerous cloud-based services that can help make them more accessible to developers and other non-data scientists. The key is identifying the right areas to augment with AI and properly executing the integration.
If you're interested in adding AI capabilities to your application, contact us to learn how we can help plan your implementation.



